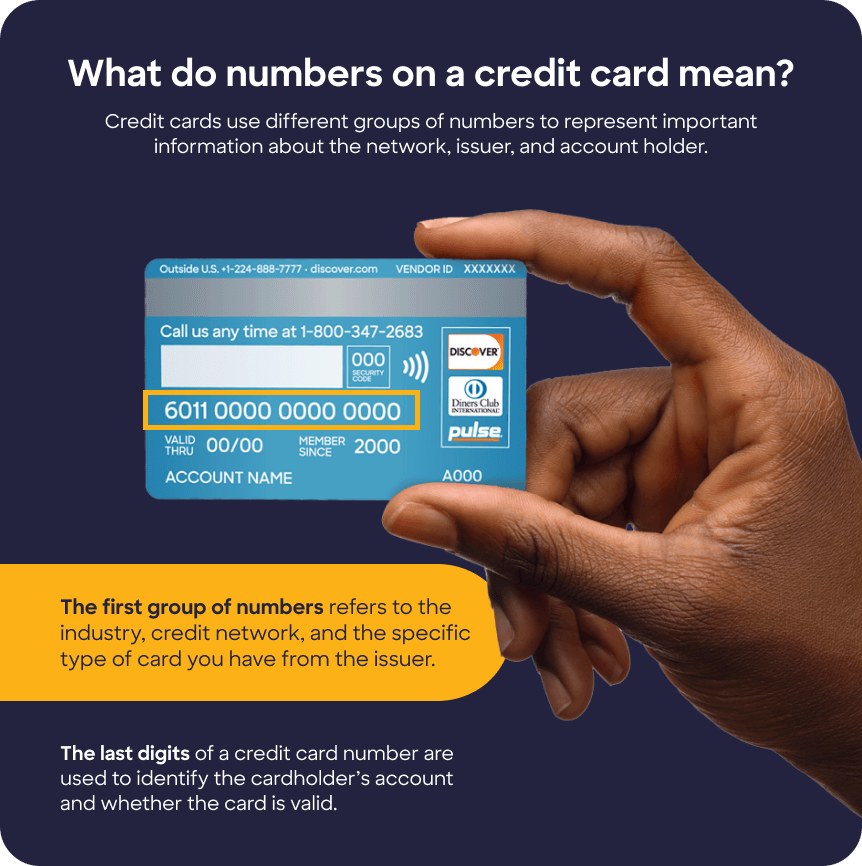
A credit card number is a set of digits displayed across the front or back of your credit card. Most credit card numbers have 16 digits, while American Express® cards have 15 digits.
Credit card companies don’t assign card numbers randomly. In fact, card numbers follow a complex pattern. These numbers identify the card issuer, the credit card network, the specific card holder’s account, and the unique card. (Debit card numbers use the same system.)
Your specific credit card number lets you make purchases and helps prevent theft and fraud.